What is the difference between ACP sheet and aluminium sheet?
Aluminium Composite Panels (ACP) and aluminium sheets are both widely used in construction and industrial applications. While they may seem similar at a glance, there are significant differences between the two materials in terms of composition, properties, applications, and advantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right material for specific projects.
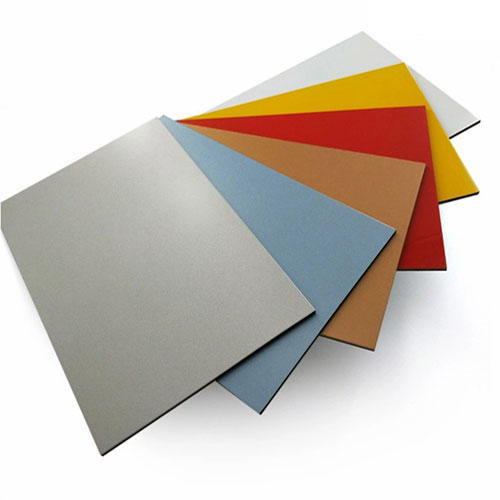
ACP Sheet:
- Layers: ACP sheets consist of two thin layers of aluminium enclosing a non-aluminium core. The core is typically made from polyethylene (PE) or a mineral-filled material for fire resistance.
- Coating: The outer aluminium layers are coated with protective paints or finishes, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal.
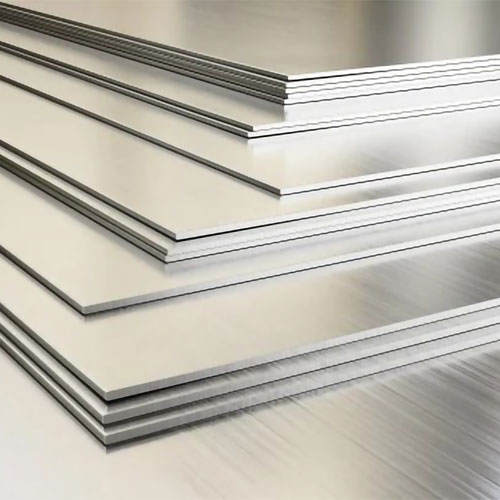
Aluminium Sheet:
- Single Material: Aluminium sheets are made entirely of aluminium, without any core material.
- Variety of Alloys: They can be produced from various aluminium alloys, each with specific properties tailored to different applications.
ACP Sheet and Aluminium Sheet Properties
ACP Sheet Properties:
- Lightweight: The non-aluminium core makes ACP sheets lighter than solid aluminium sheets of the same thickness.
- Strength and Rigidity: The composite structure provides excellent strength and rigidity, making ACP suitable for large panel applications.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation: The core material can offer improved thermal and acoustic insulation compared to solid aluminium.
Aluminium Sheet Properties:
- High Strength: Aluminium sheets offer high tensile strength and durability, depending on the alloy used.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminium naturally forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing its resistance to corrosion.
- Conductivity: Aluminium sheets have high thermal and electrical conductivity, making them suitable for specific industrial uses.
Applications
ACP Sheet Applications:
- Architectural Cladding: Widely used for building facades, curtain walls, and roofing due to its lightweight and aesthetic versatility.
- Signage: Ideal for signage and advertising panels due to its smooth surface and ease of printing.
Interior Design: Used in partitions, false ceilings, and decorative features, offering a modern look.
Aluminium Sheet Applications:
- Construction: Used in roofing, siding, and structural components where strength and durability are essential.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Utilized in the manufacturing of vehicle bodies and aircraft parts due to its strength-to-weight ratio.
- Industrial Equipment: Common in machinery, electrical enclosures, and other industrial applications requiring high conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Advantages
ACP Sheet Advantages:
- Design Flexibility: Available in various colors, textures, and finishes, allowing for creative architectural designs.
- Cost-Effective: Often more cost-effective than solid aluminium sheets for large surface areas due to the lower cost of the core material.
- Easy Installation: Lightweight nature makes ACP easy to handle and install, reducing labor and installation costs.
Aluminium Sheet Advantages:
- Superior Strength: Offers higher tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Versatility: Can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes, suitable for a wide range of industrial and commercial uses.
- High Performance: Excellent performance in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments.
Conclusion
While ACP sheets and Aluminum Sheet both serve important roles in construction and industrial applications, their distinct properties make them suitable for different purposes. ACP sheets are ideal for lightweight, aesthetic, and cost-effective cladding and signage solutions. In contrast, aluminium sheets are preferred for their superior strength, durability, and versatility in more demanding applications. Understanding these differences ensures the right material choice for specific project requirements, enhancing both performance and cost-efficiency.